For the most updated Clinical Guidance and Recommendations see the NIH Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines
Clinical Management
Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19
Summary: Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19
Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
Summary: Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
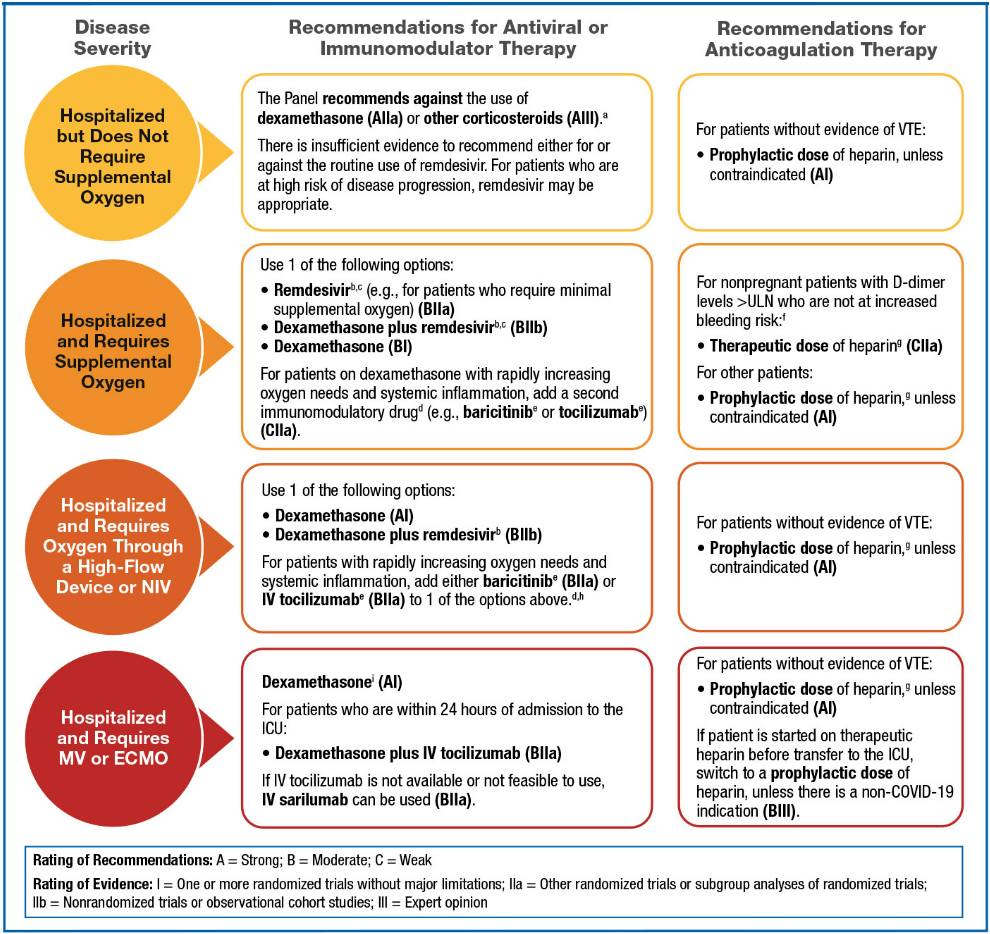
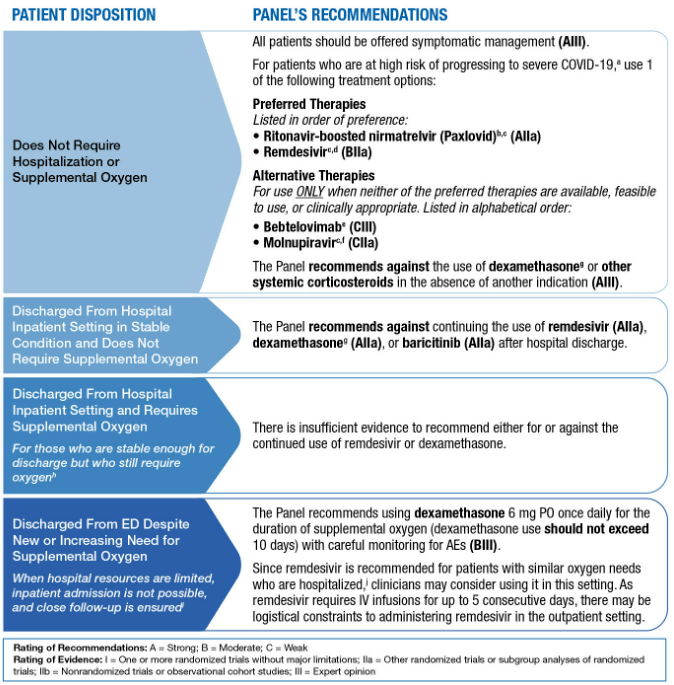
Patients Who Do Not Require Supplemental Oxygen Recommendations:
- The NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends against the use of dexamethasone (AIIa) or other corticosteroids (AIII) for the treatment of COVID-19. Patients with COVID-19 who are receiving dexamethasone or another corticosteroid for an underlying condition should continue this therapy as directed by their health care provider.
- There is insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against the routine use of remdesivir for the treatment of patients who are hospitalized for COVID-19 who do not require supplemental oxygen. However, the use of remdesivir may be appropriate in patients who are at high risk of disease progression.
Patients Who Require Supplemental Oxygen Recommendations:
- The NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends using 1 of the following options for hospitalized patients who require supplemental oxygen:
- Remdesivir (e.g., for patients who require minimal supplemental oxygen) (BIIa)
- Dexamethasone plus remdesivir (BIIb)
- Dexamethasone (BI); for patients on dexamethasone who have rapidly increasing oxygen needs and systemic inflammation, add a second immunomodulatory drug (e.g., tocilizumab or baricitinib) (CIIa)
- If dexamethasone is not available, an alternative corticosteroid (e.g., prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone) can be used (BIII). See Corticosteroids for dosing recommendations.
- For nonpregnant patients, the Panel recommends using a therapeutic dose of heparin for patients who have D-dimer levels above the upper limit of normal (ULN), require low-flow oxygen, and have no increased bleeding risk (CIIa). Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is preferred over unfractionated heparin.
For additional consideration see NIH Guidance on Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
Patients Who Require Oxygen Through a High-Flow Device or Noninvasive Ventilation Recommendations:
- The NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends using 1 of the following options for hospitalized patients who require oxygen through a high-flow device or NIV:
- Dexamethasone (AI)
- Dexamethasone plus remdesivir (BIIb)
- For patients who have rapidly increasing oxygen needs and have increased markers of inflammation, add either baricitinib (BIIa) or tocilizumab (BIIa) (drugs are listed alphabetically) to 1 of the options above.
- The Panel recommends using a prophylactic dose of heparin as VTE prophylaxis, unless a contraindication exists (AI).
- For patients who are started on a therapeutic dose of heparin in a non-ICU setting due to COVID-19 and then transferred to the ICU, the Panel recommends switching from the therapeutic dose to a prophylactic dose of heparin, unless VTE is confirmed (BIII).
- The Panel recommends against the use of an intermediate dose (e.g., enoxaparin 1 mg/kg once daily) or a therapeutic dose of anticoagulation for VTE prophylaxis, except in a clinical trial (BI).
For additional consideration see NIH Guidance on Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
Patients Who Require Mechanical Ventilation or Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Recommendations:
- The NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends using dexamethasone for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who require mechanical ventilation or ECMO (AI).
- The Panel recommends using dexamethasone plus tocilizumab for patients with COVID-19 who are within 24 hours of admission to the ICU (BIIa).
- The Panel recommends using a prophylactic dose of heparin as VTE prophylaxis, unless a contraindication exists (AI).
- The Panel recommends against the use of an intermediate dose (e.g., enoxaparin 1 mg/kg once daily) or a therapeutic dose of anticoagulation for VTE prophylaxis, except in a clinical trial (BI).
- For patients who are started on a therapeutic dose of heparin in a non-ICU setting due to COVID-19 and then transferred to the ICU, the Panel recommends switching from the therapeutic dose to a prophylactic dose of heparin, unless there is a non-COVID-19 indication (BIII).
For additional consideration see NIH Guidance on Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
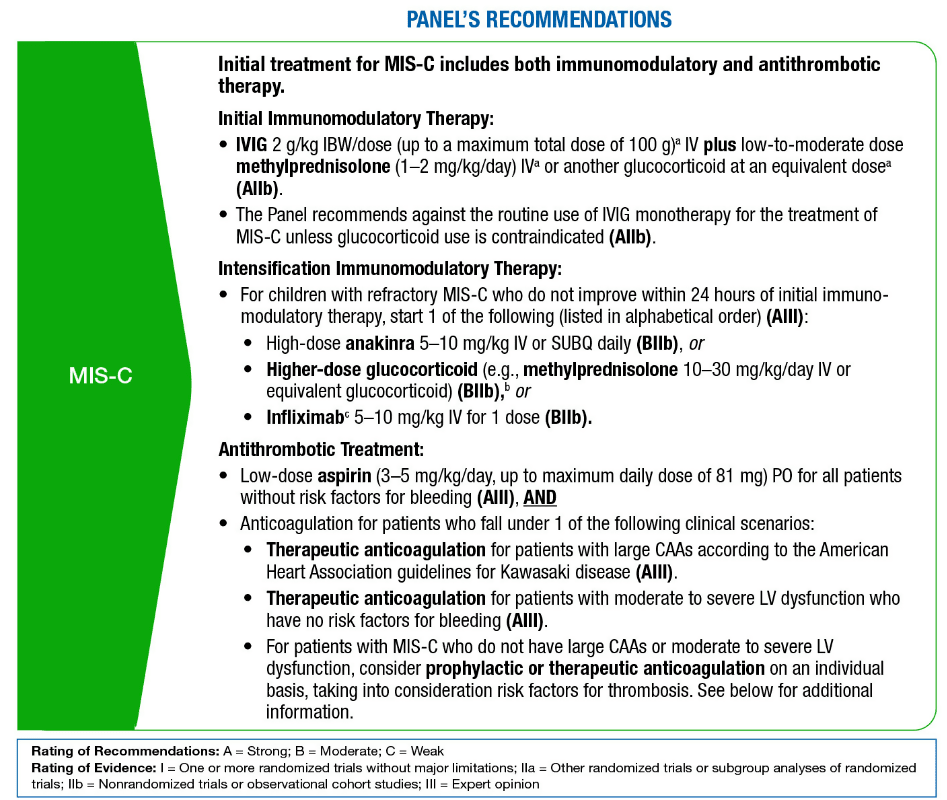
Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) (With Discussion on Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Adults [MIS-A])
Summary: Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients With MIS-C
Critical Care:
For information and guidance on Critical Care see NIH Guidelines on:
Therapies/Therapeutics:
Antiviral Therapy
Remdesivir is the only drug that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of COVID-19. Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid), molnupiravir, and certain anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have received Emergency Use Authorizations from the FDA for the treatment of COVID-19.
Summary Recommendations for Treating Nonhospitalized Patients
- The Panel recommends the use of the following anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies as preferred treatments for COVID-19. These drugs are listed in order of preference:
- Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) (AIIa)
- Remdesivir (BIIa)
- The Panel recommends the use of the following anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies as alternative treatments for COVID-19 ONLY when neither of the preferred therapies are available, feasible to use, or clinically appropriate. These drugs are listed in alphabetical order:
- Bebtelovimab (CIII)
- Molnupiravir (CIIa)
- See Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19 for detailed recommendations.
Summary Recommendations for Treating Hospitalized Patients
See Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19 for the Panel’s recommendations on using remdesivir with or without immunomodulators in certain hospitalized patients.
Antiviral Drugs That the Panel Recommends Against
- The Panel recommends against the use of the following drugs for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial:
- Interferons for nonhospitalized patients (AIIa)
- Interferon alfa or lambda for hospitalized patients (AIIa)
- Ivermectin (AIIa)
- Nitazoxanide (BIIa)
- The Panel recommends against the use of the following drugs for the treatment of COVID-19:
- Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine and/or azithromycin for hospitalized (AI) and nonhospitalized patients (AIIa)
- Lopinavir/ritonavir and other HIV protease inhibitors for hospitalized (AI) and nonhospitalized patients (AIII)
- Systemic interferon beta for hospitalized patients (AI)
For details and additional information on each antiviral please see:
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Products
Summary Recommendations for Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) for the Treatment of COVID-19
- Treatment with anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAbs should be considered for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who are hospitalized for a reason other than COVID-19 if they otherwise meet the FDA EUA criteria for outpatient treatment.
- The risk for progression to severe COVID-19 in high-risk patients is substantially greater for those who are not vaccinated or those who are vaccinated but not expected to mount an adequate immune response to the vaccine due to an underlying immunocompromising condition.
- At this time, the NIH COVID Guidelines Panel’s anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAb recommendations are for the treatment of nonhospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of progressing to severe disease.
Summary Recommendations for Bebtelovimab
- The Panel recommends using bebtelovimab 175 mg intravenous injection in patients aged ≥12 years as an alternative therapy ONLY when ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) and remdesivir are not available, feasible to use, or clinically appropriate (CIII). Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible and within 7 days of symptom onset. For additional information see the NIH Guidance on Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19.
- Bebtelovimab should be administered in a setting where severe hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, can be managed. Patients should be monitored during the injection and observed for at least 1 hour after injection.
Summary Recommendations for Bamlanivimab Plus Etesevimab, Casirivimab Plus Imdevimab, and Sotrovimab
- Because the Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant of concern (VOC) and its subvariants have become dominant in the United States, the Panel recommends against using bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab, or sotrovimab for the treatment of COVID-19 (AIII).
Summary Recommendations for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies as Post-Exposure Prophylaxis for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- The Panel recommends against the use of bamlanivimab plus etesevimab and casirivimab plus imdevimab for SARS-CoV-2 post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), as the Omicron VOC, which is not susceptible to these agents, is currently the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant circulating in the United States (AIII).
Summary Recommendations for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- The Panel recommends using tixagevimab 300 mg plus cilgavimab 300 mg (Evusheld) administered as 2 consecutive 3-mL intramuscular injections (BIII) as SARS-CoV-2 pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for adults and adolescents (aged ≥12 years and weighing ≥40 kg) who do not have SARS-CoV-2 infection, who have not been recently exposed to an individual with SARS-CoV-2 infection, AND who:
- Are moderately to severely immunocompromised and may have an inadequate immune response to COVID-19 vaccination; or
- Are not able to be fully vaccinated with any available COVID-19 vaccines due to a history of severe adverse reactions to a COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- For individuals who previously received a dose of tixagevimab 150 mg plus cilgavimab 150 mg, the FDA EUA states that a second dose should be administered as soon as possible:
- If the initial dose was administered ≤3 months ago, the second dose should be tixagevimab 150 mg plus cilgavimab 150 mg.
- If the initial dose was administered >3 months ago, the second dose should be tixagevimab 300 mg plus cilgavimab 300 mg.
- Tixagevimab plus cilgavimab is not a substitute for COVID-19 vaccination and should not be used in unvaccinated individuals for whom COVID-19 vaccination is recommended and who are anticipated to have an adequate response.
- If supplies of tixagevimab plus cilgavimab are limited, priority for use as PrEP should be given to those who are at the highest risk for severe COVID-19 (for additional information see Prioritization of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapies for the Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19 When There Are Logistical or Supply Constraints).
Summary Recommendations for COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma
- The Panel recommends against the use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP) that was collected prior to the emergence of the Omicron VOC for the treatment of COVID-19 (AIII).
- The Panel recommends against the use of CCP for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized, immunocompetent patients (AI).
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of high-titer CCP that was collected after the emergence of the Omicron VOC for the treatment of immunocompromised patients and nonhospitalized, immunocompetent patients with COVID-19.
Summary Recommendations for Anti-SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immunoglobulins
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific immunoglobulins for the treatment of COVID-19.
For details and additional information on each Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody product please see:
Immunomodulators
Summary Recommendations
There is insufficient evidence for the NIH COVID Guidelines Panel to recommend either for or against the use of the following immunomodulators for the treatment of COVID-19:
- Anakinra
- Fluvoxamine
- Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhibitors for hospitalized patients
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- The Panel recommends against the use of the following immunomodulators for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial:
- Baricitinib plus tocilizumab (AIII)
- Canakinumab (BIIa)
- Colchicine for nonhospitalized patients (BIIa)
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (non-SARS-CoV-2-specific) for the treatment of patients with acute COVID-19 (AIII). This recommendation should not preclude the use of IVIG for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) or when it is otherwise indicated.
- Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., acalabrutinib, ibrutinib, zanubrutinib) (AIII)
- JAK inhibitors other than baricitinib and tofacitinib (e.g., ruxolitinib) (AIII)
- Siltuximab (BIII)
The Panel recommends against the use of the following immunomodulators for the treatment of COVID-19:
- Colchicine for hospitalized patients (AI)
Summary Recommendations for Colchicine
- The Panel recommends against the use of colchicine for the treatment of nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (BIIa).
- The Panel recommends against the use of colchicine for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (AI).
Summary Recommendations for Corticosteroids
- For Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19 in these patients.
- Patients with COVID-19 who are receiving dexamethasone or another corticosteroid for an underlying condition should continue this therapy as directed by their health care provider (AIII).
- For additional information on the use of dexamethasone or other systemic corticosteroids in certain nonhospitalized patients see the NIH Guidance on see Therapeutic Management of Nonhospitalized Adults With COVID-19.
- For Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19
- Inhaled Corticosteroids in Patients With COVID-19
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19.
Summary Recommendations for:
-
- There is insufficient evidence for the COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) to recommend either for or against the use of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19.
- Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Inhibitors
-
- There is insufficient evidence for the COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) to recommend either for or against the use of GM-CSF inhibitors for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
- Immunoglobulins: Non-SARS-CoV-2 Specific
-
- The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends against the use of non-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-specific intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for the treatment of acute COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (AIII).
- This recommendation should not preclude the use of IVIG when otherwise indicated for the treatment of complications that arise during the course of COVID-19.
-
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of anakinra for the treatment of COVID-19.
- The Panel recommends against the use of canakinumab for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (BIIa).
-
- The Panel recommends against the use of anti-IL-6 mAb therapy (i.e., siltuximab) for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (BIII).
- For information on the use of IL-6 inhibitors (e.g., sarilumab, tocilizumab) in hospitalized patients who require supplemental oxygen, high-flow oxygen, noninvasive ventilation (NIV), or mechanical ventilation see NIH Guidance on the Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19.
- Janus Kinase Inhibitors
- Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- The Panel recommends against the use of BTK inhibitors for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (AIII).
For details and additional information on each Immunomodulator please see:
Antithrombotic Therapy
Summary Recommendations for Chronic Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy
- The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) recommends that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are receiving anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy for underlying medical conditions continue this treatment unless significant bleeding develops, or other contraindications are present (AIII).
Summary Recommendations for Screening and Evaluation for Venous Thromboembolism
- In patients with COVID-19 who have no signs or symptoms of venous thromboembolism (VTE), there is currently insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against routine VTE screening, regardless of the patient’s coagulation markers.
- For hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who experience rapid deterioration of pulmonary, cardiac, or neurological function or sudden, localized loss of peripheral perfusion, the Panel recommends evaluating the patients for thromboembolic disease (AIII).
Summary Recommendations for Anticoagulant Treatment for Thrombosis
- The Panel recommends that when diagnostic imaging is not possible, patients with COVID-19 who are highly suspected to have thromboembolic disease be managed with therapeutic anticoagulation (AIII).
- The Panel recommends that patients with COVID-19 who require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or continuous renal replacement therapy or who have thrombosis related to catheters or extracorporeal filters be treated with antithrombotic therapy as per the standard institutional protocols for those without COVID-19 (AIII).
Summary Recommendations for Antithrombotic Therapy for Nonhospitalized Patients Without Evidence of Venous Thromboembolism
- In nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, the Panel recommends against the use of anticoagulants and antiplatelet therapy (aspirin or P2Y12 inhibitors) for the prevention of VTE or arterial thrombosis unless the patient has other indications for the therapy or is participating in a clinical trial (AIIa).
- The Panel recommends against routinely continuing VTE prophylaxis for patients with COVID-19 after hospital discharge, except in a clinical trial (AIII).
- For patients who are at high risk for VTE and low risk for bleeding, there is insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against continuing anticoagulation after hospital discharge unless another indication for VTE prophylaxis exists.
Summary Recommendations for Antithrombotic Therapy for Hospitalized, Nonpregnant Adults Without Evidence of Venous Thromboembolism
- The Panel recommends against using anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy to prevent arterial thrombosis outside of the usual standard of care for patients without COVID-19 (AIII).
- In hospitalized patients, low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or unfractionated heparin (UFH) is preferred over oral anticoagulants, because these 2 types of heparin have shorter half-lives and the effect can be reversed quickly, can be administered intravenously or subcutaneously, and have fewer drug-drug interactions (AIII).
- When heparin is used, LMWH is preferred over UFH.
For adults who require low-flow oxygen and do not require intensive care unit (ICU)-level care:
- The Panel recommends using a therapeutic dose of heparin for patients with D-dimer levels above the upper limit of normal, who require low-flow oxygen, and who do not have an increased bleeding risk (CIIa).
- Contraindications for the use of therapeutic anticoagulation in patients with COVID-19 are a platelet count <50 x 109/L, hemoglobin <8 g/dL, the need for dual antiplatelet therapy, bleeding within the past 30 days that required an emergency department visit or hospitalization, history of a bleeding disorder, or an inherited or active acquired bleeding disorder. This list is based on the exclusion criteria from clinical trials; patients with these conditions have an increased risk of bleeding.
- In patients without VTE who have begun a therapeutic dose of heparin, treatment should continue for 14 days or until hospital discharge, whichever comes first.
- The Panel recommends using a prophylactic dose of heparin for patients who are not receiving a therapeutic dose of heparin, unless a contraindication exists (AIIb).
- The Panel recommends against the use of a therapeutic dose of oral anticoagulants for VTE prophylaxis or prevention of COVID-19 progression, except in a clinical trial (AIIa).
- There is currently insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against the use of thrombolytics for COVID-19.
- The Panel recommends against the use of antiplatelet therapy to prevent COVID-19 progression or death in noncritically ill patients (BIIa).
For adults who require ICU-level care, including those receiving high-flow oxygen:
- The Panel recommends using a prophylactic dose of heparin as VTE prophylaxis, unless a contraindication exists (AI).
- The Panel recommends against the use of an intermediate dose (e.g., enoxaparin 1 mg/kg once daily) or a therapeutic dose of anticoagulation for VTE prophylaxis, except in a clinical trial (BI).
- For patients who start on a therapeutic dose of heparin in a non-ICU setting due to COVID-19 and then transfer to the ICU, the Panel recommends switching from the therapeutic dose to a prophylactic dose of heparin, unless VTE is confirmed (BIII).
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against antiplatelet therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
Summary Recommendations for Hospitalized Children
- For hospitalized children with COVID-19, indications for VTE prophylaxis should be the same as those for children without COVID-19 (BIII).
Summary Recommendations for Special Considerations During Pregnancy and Lactation
- The Panel recommends that pregnant patients who are receiving anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapies for underlying conditions continue these medications after they receive a diagnosis of COVID-19 (AIII).
- The Panel recommends using a prophylactic dose of anticoagulation for pregnant patients hospitalized for manifestations of COVID-19, unless otherwise contraindicated (BIII).
- Because pregnant patients have not been included in most clinical trials evaluating therapeutic anticoagulation in the setting of COVID-19, there is currently insufficient evidence to recommend either for or against therapeutic anticoagulation for pregnant patients with COVID-19 without evidence of VTE.
- Like for nonpregnant patients, VTE prophylaxis after hospital discharge is not routinely recommended for pregnant patients (BIII). Decisions to continue VTE prophylaxis in the pregnant or postpartum patient after discharge should be individualized, with consideration of concomitant VTE risk factors.
- The use of anticoagulation therapy during labor and delivery requires specialized care and planning. It should be managed in pregnant patients with COVID-19 in a similar way as in pregnant patients with other conditions (AIII).
- UFH, LMWH, and warfarin do not accumulate in breast milk and do not induce an anticoagulant effect in the newborn; therefore, they can be used by breastfeeding individuals who require VTE prophylaxis or treatment (AIII).
For details and additional information see NIH Guidance on Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients With COVID-19
Supplements
Summary Recommendation for Vitamin C
- There is insufficient evidence for the COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) to recommend either for or against the use of vitamin C for the treatment of COVID-19.
Summary Recommendation for Vitamin D
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of vitamin D for the treatment of COVID-19.
Summary Recommendation for Zinc
- There is insufficient evidence for the Panel to recommend either for or against the use of zinc for the treatment of COVID-19.
- The Panel recommends against using zinc supplementation above the recommended dietary allowance for the prevention of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (BIII).
For additional information use of Supplement please see NIH Guidance on Supplements
Use of Concomitant Medications in Patients With COVID-19
Summary Recommendations
- Patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant medications (e.g., angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs], HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors [statins], systemic or inhaled corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acid-suppressive therapy) for underlying medical conditions should not discontinue these medications during acute management of COVID-19 unless discontinuation is otherwise warranted by their clinical condition (AIIa for ACE inhibitors and ARBs; AIII for other medications).
- The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recommends against using medications off-label to treat COVID-19 if they have not been shown to be safe and effective for this indication in a clinical trial (AIII).
For additional information Using Concomitant Medications in Patients With COVID-19 please see NIH Guidance on Concomitant Medications


