ACEP ID:
- My Account
- My CME
- Sign Out
ACEP ID:
Incubation period averages 7−14 days but can range from 5−21 days.
Prodrome/Invasion period (lasts between 0–5 days)
Rash/Skin Eruption
Rash evolution
Stage
Stage Duration
Characteristics
Enanthem
The first lesions to develop are on the tongue and in the mouth.
Macules
1−2 days
Following the enanthem, a macular rash appears on the skin, starting on the face and spreading to the arms and legs and then to the hands and feet, including the palms and soles.
The rash typically spreads to all parts of the body within 24 hours becoming most concentrated on the face, arms, and legs (centrifugal distribution).
Papules
1−2 days
By the 3rd day of rash, lesions have progressed from macular (flat) to papular (raised).
Vesicles
1−2 days
By the 4th-5th day, lesions have become vesicular (raised and filled with clear fluid).
Pustules
5−7 days
By the 6th-7th day, lesions have become pustular (filled with opaque fluid) – sharply raised, usually round, and firm to the touch (deep seated).
Lesions will develop a depression in the center (umbilication).
The pustules will remain for approximately 5 to 7 days before beginning to crust.
Scabs
7−14 days
By the end of the 2nd week, pustules have crusted and scabbed over.
Scabs will remain for about a week before beginning to fall off.
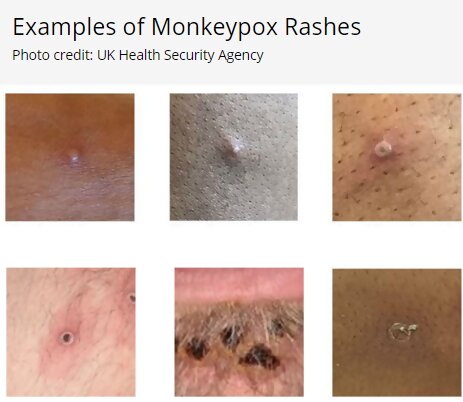
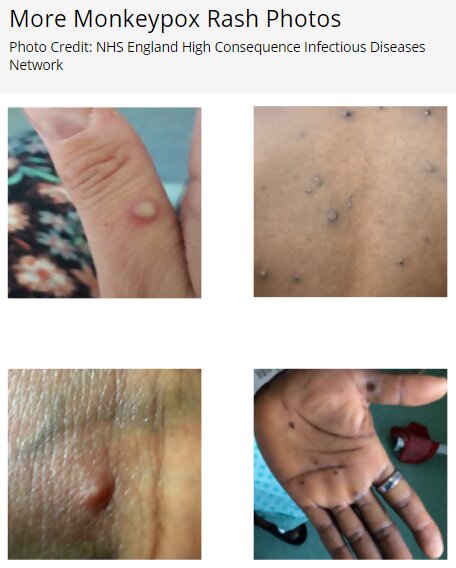
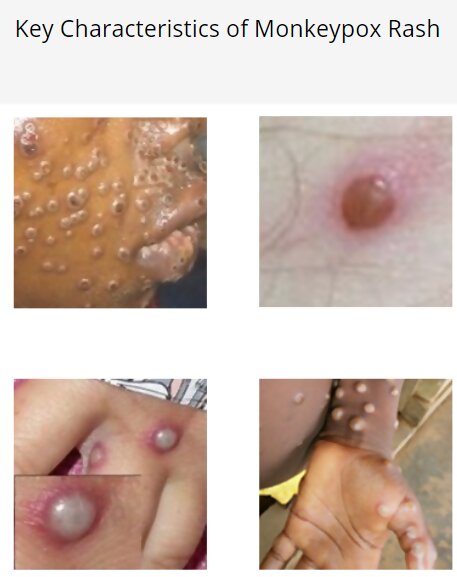
For additional information and answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Monkeypox for Healthcare Professionals, see CDC Clinician FAQs.